LS Training Manual

CHAPTER 1: Introduction
Dr. Chim Ho Yeung, Hastings
(Project Investigator)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Dr. Hastings Chim has been a registered primary and secondary school teacher for more than 22 years. He served as an English panel head in a secondary school and is currently a senior lecturer at EdUHK, taking up the roles of Field Experience Coordinator for the SEC Department and previously
Co-Coordinator of the BAT program. He accomplished his Doctorate specializing in Inclusive Teacher Training at the University of Bristol.

Dr. Ho Fuk Chuen
(Consultant, Adjunct Assistant Professor)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Dr. Ho was previously the Programme Coordinator of the Professional Development Course (Catering for Children with Learning Needs) and Programme Coordinator of the Basic, Advanced and Thematic Courses for Teachers of Students with Special Educational Needs. He was formerly an inspector in the Special Education Inspectorate of the Hong Kong Education Bureau. Dr. Ho was the project leader of several external funded projects in the areas of dyslexia, Theory of Mind and collaborative mode of professional development for teachers.

Dr. Leung Sheung Kwan, Sharon
(Senior Lecturer II)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Dr. Sharon Leung is a senior lecturer in teacher education. Her teaching areas include managing student diversity, differentiated instruction, curriculum adaptation and assessment. With teaching experiences in mainstream schools, special schools and tertiary institutions, she is interested in promoting collaborative action research for enhancing student learning as well as teaching practice in the context of today’s school environment.

Dr. Siu F Lin, PhD AFBPsS
Chartered Psychologist
(School Case Manager)
Senior Lecturer II
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Dr. SF Lin is a chartered psychologist and an associate fellow of the British Psychological Society. She obtained her PhD at The University of Birmingham in the UK. Dr Lin has been supporting children with special needs & conducting teacher & parent consultations for decades. Dr Lin has published in both English & Chinese languages for encyclopedias, journals & books. Subjects include art education, youth suicide, dating behaviour & sexual education, children’s learning, parenting & emotional needs of children & adolescents.

Mr. Chan Wai Man, Avstin (Guest Lecturer)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Mr. Chan has been a registered secondary school teacher for more than 34 years. Being the vice principal in school, he has rich experience in planning, implementing and monitoring programmes related to students’ growth and development. He would like to devote his time in education
after retirement because of his great passion in education..

Ms. Ching Sau Man (Guest Lecturer)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Ms. Ching Sau Man has served in special schools and mainstream schools for more than 30 years. She has also held management positions such as principal of education center, vice principal of primary school, and executive director of charity organisation. She has extensive experience in the implementation of inclusive education, gifted education, community service and parental support. Ms. Ching Sau Man is currently an instructor of the University for the Special Education and Gifted Education In-service Teachers Professional Training Programme.

Ms. Jessie Fung Kwei Yi, Jessie
(Guest Lecturer)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Ms. Jessie Fung is presently the Project leader of Launching an Education and Research Base for Early Intervention in the Greater Bay Area. She formerly was a Senior Lecturer at the Department of Special Education and Counselling and the Department of Early Childhood Education and later acted as Project Manager of the Centre for Special Educational Needs and Inclusive Education
at The Education University of Hong Kong. She has over 20 years of teacher training experience in early childhood education, developmental psychology, parent counselling, and special and integrated education. She has also extensive working experience in education project consultancy for school based and NGOs.

Dr. Ho Pik Ying (Guest Lecturer)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Dr. Ho has been a registered primary and kindergarten teacher. Dr. Ho’s research interests include early intervention and electronic IEP System. She has been working in different fields of education and has extensive professional experience in frontline teaching, teacher training and parent education. Dr. Ho has been teaching undergraduate and postgraduate education programmes for various universities and higher education institutions. She also provides parent education, in-service training and consultation services to schools, as well as centres for children residential services.

Mr. So Kin Kwan, Kennith (Guest Lecturer)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Mr. So has almost 40 years’ experience in the field of education, and he is especially knowledgeable about special education. He had been a school principal in special schools and an inspector of the Quality Assurance Division of Education Bureau, Hong Kong, which enabled him to gain a lot of experience in assessing the quality of school performance, including the support for SEN under the policy of integrated education. Mr. So has coordinated a few school support projects while he is working at EdUHK. Currently, he is also a guest lecturer at the University.

Mr. Lau Hor Keung
(Guest Lecturer)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Mr. Lau is a retired secondary school principal. He is currently the practicum supervisor for the Advanced and Thematic Courses for in-service training on catering for learning diversities. Mr. Lau coordinated and taught the Service- based Learning in Afterschool Service to SEN Students Course for the undergraduate students of the EdUHK. He is participating in a number of professional development courses and school support projects of the University.

Dr. Lee Lai Mui, Frances
(Guest Lecturer)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Frances was a secondary school teacher, counselling mistress and curriculum development office for over 20 years. Her research has centered on how self-concept, motivation and other socio-cultural practices can influence and enhance children’s psychological development. Frances has published several papers exploring these topics from different perspectives and am currently working on consolidating this work and developing it into a book project.
Because of her expertise, Frances has been invited to provide consultation and
training for a number of groups and schools, worked with the community to
advocate the needs of children.

Mr. WONG Chun Man Vincent
(Guest Lecturer)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Mr. Wong, a retired secondary school principal, now serves as the School Supervisor of an aided secondary school that attracts students from 20 different countries, many of whom have diverse learning needs. Additionally, he also serves as the school manager of three other aided secondary schools. In addition to his voluntary community work, Mr. Wong holds two positions: (i) practicum supervisor in both the advanced course on Catering for Diverse Learning Needs and the Thematic Course on Supporting Students with SEN – Cognition and Learning Needs (Facilitating English Language Learning – Focusing on the needs of students with Specific Learning Difficulties) at the Education University of Hong Kong, and (ii) guest speaker and instructional associate in the “Preparation for Principalship Course for Aspiring Principals (PFP) at the Chinese University of Hong Kong.”

Ms. Tam Gee May (Assistant Project Manager)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Ms. Gee May Tam is a Board Certified Behaviour Analyst and a registered Psychologist with the New Zealand Psychologists Board. She has over 10 years’ experience in providing behavioural therapy for children and adults with developmental and/or intellectual disabilities in homes and schools. She has also provided supporting services for schools and families of children with special educational needs in Hong Kong.

Miss Ng Lok Yiu, Yoyo (Project Assistant)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Miss Ng Lok Yiu, Yoyo is a Social Science graduate from The Education University of Hong Kong. She previously worked in the Environmental field in cooperation with the AFCD. Yoyo has faith in that students with diverse learning needs could be helped based on cohesive partnership between their home and school to a great extent.

Miss Hui Cheuk Lam (Project Assistant)
Department of Special Education and Counselling
The Education University of Hong Kong
Miss Hui Cheuk Lam is a Humanities and Social Science graduate from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST). She starts her career at the Education University of Hong Kong (EdUHK) in 2023 and believes that students with different developmental levels can grow and flourish through different educational methods and curriculum designs.
Learning Support Introduction
The Jockey Club “Diversity at Schools” Project which is funded by The Hong Kong Jockey Club Charities Trust is a joint collaboration among the Faculty of Education from The University of Hong Kong, the Department of Computing from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, and the Department of Special Education and Counselling from The Education University of Hong Kong.
This project will continue to consolidate the “School-based Diversified Management Framework” (DM Infrastructure) through the three project initiatives
of “Student Data”, “Differentiated Instruction” and “Learning Support”, as well as the establishment of a support mode and nurturement of teachers’ self-directed learning to further enhance the capacity of schools and teachers to cater for students’ learning diversity, so that each student can learn in an active and meaningful way.
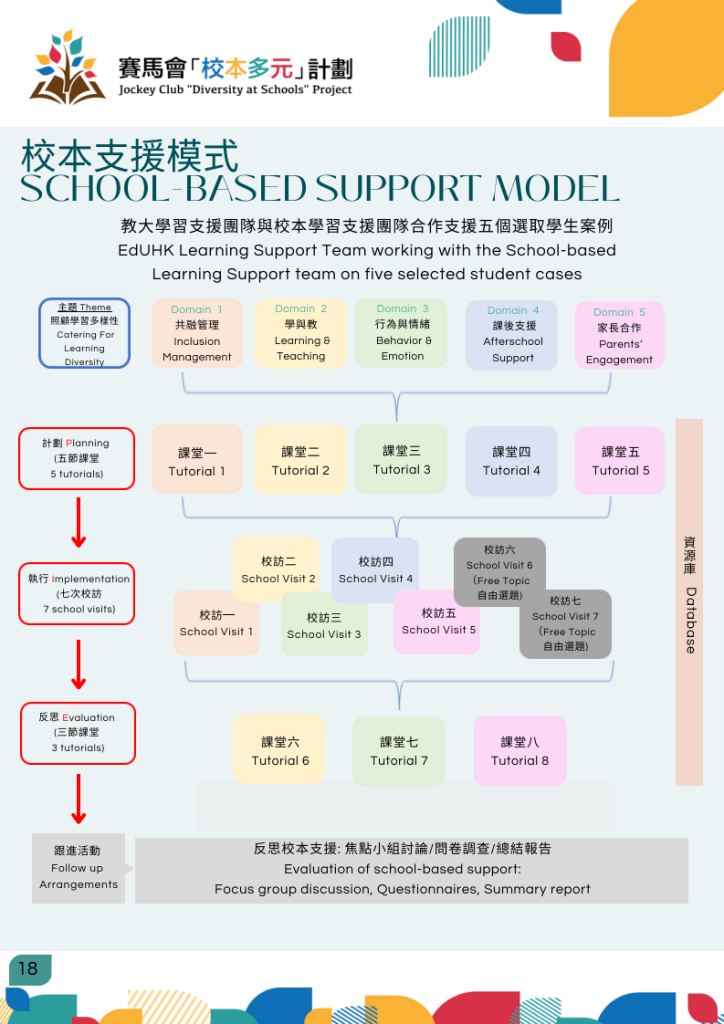
In this project, the Learning Support (LS) Team provides professional training, customized school visits and regular review services to the participating schools based on the team’s professional advices on how these participating schools cater for learning diversities.
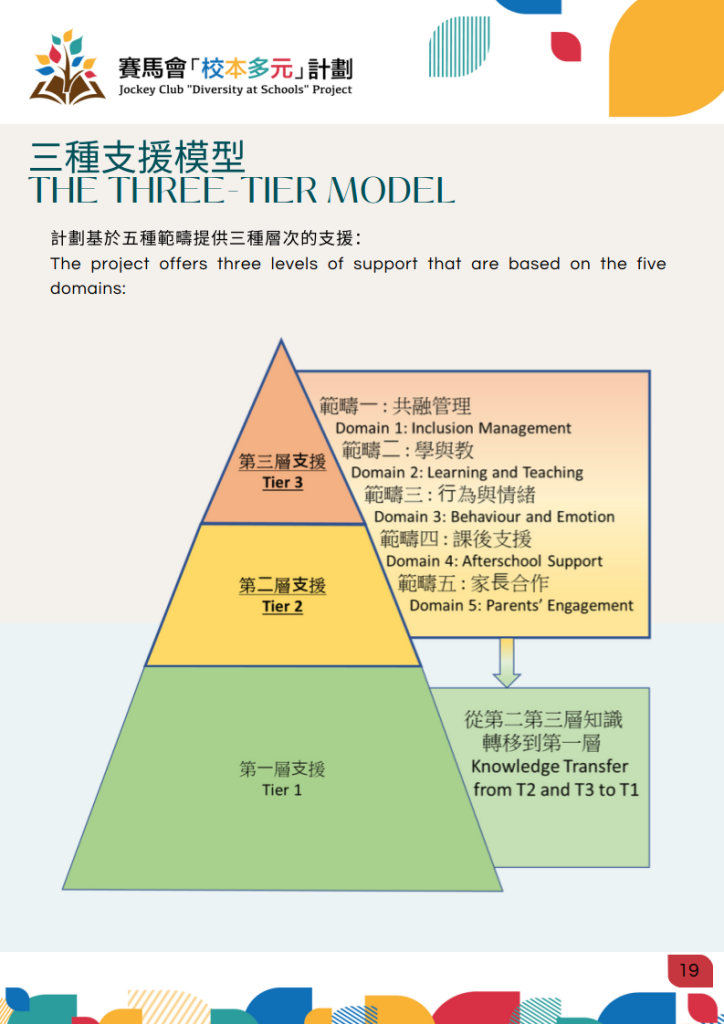
Based on the five student cases selected from each school, the LS Team assists all participating schools to support and evaluate these five cases in terms of five domains: Inclusion Management, Learning and Teaching, eIEP (electronic Individualized Education Plan), Afterschool Support and Parents’ Engagement
across tutorials and school visits, and in consideration of the roles played by three distinctive members: SENCOs (Special Educational Needs Coordinator), SENSTs (Special Educational Needs Support Teachers) and LSAs (Learning Support Assistants).
ONE THEME
FIVE DOMAINS
3-Tier Model
LEARNING SUPPORT MODEL
The Learning Support model is designed in a way to comply with Hargreaves & O’Connor’s ten tenets of collaborative professionalism (Hargreaves &
O’Connor, 2017) in which the team will work closely with the participating schools in high-level project planning and execution. We will work together to
develop a course blueprint which will be a piece of thoughtful work that involves dialogue and action. In the customized school visits, the team and
the observed will enter into a genuine dialogue or engage in a heated debate about the best way to help the diverse learners.
Hargreaves, A., & O’Connor, M. T. (2017). Collaborative professionalism. World Innovation Summit for Education. An Initiative of Qatar Foundation. Retrieved from https://www.wise-qatar.org/2017-wise-research-collaborative-professionalism.
THE OUTPUT OF THIS PROJECT
(A) What we offer
Resource Sharing
– Build a cross-school learning community
– Optimize the electronic database
5 School Visits
– Assist schools to implement the “Learning Diversity Support” strategy
10 Training Sessions
– Inspire/assist schools to implement school-based “Learning Diversity Support”
Summary Report
– Evaluation of Learning Diversity Support Development
– Summary of Five Domains
(B) (What we will collect from your schools to build the school-based platform’)
5 eIEP Cases
– New/Old Cases
(Revised version)
5 Lesson Plans
– Selected from 12 lesson plans
from the DI* team or
– Existing lesson plans
5 Afterschool Support Plans
– Tier 2/3/Interest/Service/
Counselling Group
– Catering to students’ behavioural and emotional needs
CHAPTER 2
Domain 1: Inclusion Management
In this chapter, we will focus on how the three distinctive roles (SENCOs, SENST, LSTs) could collaborate to assist the student cases in each school in terms of their manpower allocation and positioning.
Domain 1: Inclusion Management
TUTORIAL
Aim of our EdUHK’s LS team: facilitate school’s LS team by developing a model to enhance catering for learner diversity in school
Our vision and mission
Workshop structure – across sessions and within sessions
What to expect in our sessions: sharing, reflection, discussions, role play, videos….
About our EdUHK’s team: who to contact
Introduction
- What are the three roles in the five student cases?
- How do these roles function to support student cases?
Roles
SENCO
Alignment with different stakeholders
- School’s vision and mission
- Similarities and differences
- Conclusion all schools and within schools are different.
- Redefining the role of SENCO
- Current effective strategies for collaboration and coordinating in terms of soft skills eg communication, administrative skills (e.g., planning and organization) and hard skills eg IT
- Limitations
- Future suggestions
SENST
- Redefining the role of SENST in inclusion management
- Current effective strategies for working with SENCO, teachers, LSA and parents, etc
- Limitations
- Future suggestions
LSA
- Redefining the role of LSA in inclusion management
- Current effective strategies for working with SENCO, teachers, SENST and parents, etc
- Limitations
- Future suggestions


Highlights of the discussion (School management examples)
Video Highlight on tutorial
Domain 1: Inclusion Management
SCHOOL VISIT
Introduction
- Discussion of School-Based Learning Management & Measures
- Preparation before lesson observation
- Tour of the school to view its facilities, etc.
Roles
SENCO
Alignment with different stakeholders
- Communication and hard skills e.g. IT
- Resources allocation
- Manpower allocation
- Effective communication
Arrangement of School Visit 1
School-based planning day
1. Understand the school facilities (SENCO)
1.1 Poster to praise outstanding students at each level: It is recommended to include sharing of students’ problem-solving experiences so that students can see the successful cases of their peers.
2. Interview with the two vice-principals and a group photo
3. Prepare meetings with teachers
3.1 Set the goal of visiting the school: (PSMCD)
-Using five student cases as cases to create a “school-based support strategy” for teacher professional development
-Determine students’ primary school entrance and promotion “transfer plan”
-The eIEP system installation is progressing smoothly
3.2 Introduce the key points of filling in the student and parent consent form and the class observing teacher consent form, which need to be filled in before observing the class (SENCO)
3.3 Organizing student personal folders: It is recommended to add separate pages to facilitate future archiving and review:
-Student profile
-Evaluation information
-Support plan
-Others (other pages can be added according to school-based needs in the future)
4. Discussion on student cases:
-Student Case 1
(Student support team teachers, SENCO, Chinese subject teacher, English subject teacher, Mathematics subject teacher)
Domain 2 (L&T), 3 (B&E), 4 (AS): LSA Mentorship
SCHOOL VISIT
Introduction
SENCO
- Two hours customized LSA mentorship Or
- Any concern SENCO like to address
Arrangement of School Visit 2
LSA Training
- LSA Mentorship Professional Workshop
1.1 Planning for development of the highlights of students
1.2 Instructions for contacting parents
1.3 Number of people: 2
2. <Learning Support Assistant Manual> Preparation:
2.1 Complete the first draft (refer to the hyperlink in “Learning Support Assistant Training Notes”)
2.2 Please indicate the teacher’s name on the cover to avoid losing it.
2.3 Scope of work: List the different scopes of work of the five teachers.
2.4 Loose-leaf folders can be used to store various forms and documents in the manual for easy updating.
2.5 You can add a summary description of the students the teacher is responsible for to facilitate immediate understanding when joining the job.
2.6 Add the lecture notes for contacting parents (see pages 144 – 145 of the notes)
2.7 Crisis management can be added to school-based information paths and leaflets, such as handling epileptic seizures, identifying, supporting and referring students with suicidal behavior (see WhatsApp document for teacher)
3. Student case discussion: Cases 1, 3, and 4

CHAPTER 3: Inclusive Learning & Teaching
In this chapter, we will discuss how the three distinctive roles (SENCOs, SENST, LSTs) could collaborate to assist the five selected cases in each school in terms of the inclusive teaching strategies and their adoption in tier 2 withdrawal classes.
Domain 2: Inclusive L&T
TUTORIAL
Introduction
- What are the three roles in supporting the L&T for five cases?
- What are effective teaching strategies in small class setting for these five cases?
- How do we assess the effectiveness?
Roles
SENCO
- Coordination with Teachers, LS Team, Parents
- Understanding the child’s learning needs, eg Learning Style and Ability Level and communicating with class teacher and LS team
- Effective and efficient methods of learning assessments
- Sharing of effective teaching strategies to class teacher and LS team
- Bring effective teaching strategies to classroom and home
SENST
- Working with class teacher, SENCO and LSA
- Understanding the child’s learning needs, eg Learning Style and Ability Level
- Effective and efficient methods of learning assessments
- Case sharing of effective teaching strategies previously used
LSA
- Working with class teacher, SENCO, SENST
- Understanding the child’s learning needs, eg Learning Style and Ability Level
- Effective and efficient methods of learning assessments
- Learning of effective teaching strategies
- Recap of last session
Highlights of the discussion
Discussed lesson plan samples
Secondary schools
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
Video Highlight on tutorial

CHAPTER 4: Behavorial and Emotional Support for student cases
In this chapter, we will discuss how the three distinctive roles (SENCOs, SENST, LSTs) could collaborate to assist the five selected cases in each school in terms of the electronic Individualized Educational Plan (eIEP) in tier 3 setting.
Domain 3: Inclusive B&E
TUTORIAL
Introduction
- Briefing of the eIEPs
- 5 cases introduction
- Needs analysis
Roles
SENCO
- Coordinate with Teacher, LS team, Student, Parent, Professionals
- Effective and efficient methods of identifying behavioural and emotional needs
- Sharing of effective B&E management strategies to class teacher and LS team
- Bring effective B&E management strategies to classroom and home
SENST
- Working with Teacher, SENCO, LSA, Student, Parent, Professionals
- Effective and efficient methods of identifying behavioural and emotional needs
- Applying learnt strategies to withdrawal classes or small group skills training (T2)
- Case sharing of effective B&E management strategies
LSA
- Working with Teacher, SENST, SENCO, Student, Parent, Professionals
- Effective and efficient methods of identifying behavioural and emotional needs
- Learning of effective B&E management strategies to use in the classroom or 1:1 training
Video Highlight on tutorial
Highlights of the discussion
Domain 3: Inclusive B&E
SCHOOL VISIT
Introduction
- Lesson observation
- Post observation meeting
- Preparation before Afterschool Support observation
SENCO
- Assessments and learning measures OR
- Skills transfer from T2 to T1 class x 5 lesson samples OR
- Any concern they like to address

CHAPTER 5
Domain 4: Afterschool Support
Domain 4:T2 Support
TUTORIAL
Introduction
- What are the three roles in supporting the B&E for five cases?
- What are the effective small group settings for these five cases?
- How do we assess the effectiveness?
Roles
SENCO
- Coordinate with instructors, professionals, LS team, teachers, parents
- Sharing of student’s acquired skills to LS team, class teachers, parents
- Determining how acquired skills can be applied in classroom and home
- Facilitation of skills transfer from small group to classroom and home
- Developing anti-bullying mechanism
SENST
- Working with SENCO, LSA, teachers
- Maintenance and transfer of acquired skills in classroom
- Case sharing of maintenance and generalisation of acquired skills in the classroom
- Skills of anti-bullying
LSA
- Working with SENCO, SENST, teachers
- Maintenance of acquired skills in classroom
- Learning to support maintenance and generalisation of students’ acquired skills in the classroom
- Support of anti-bullying
Highlights of the discussion
Discussed Afterschool Support/small class plans
Secondary schools
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
Domain 4: T2 support
SCHOOL VISIT
Introduction
- Afterschool Support observation
- Post observation meeting
- Preparation for the three interviews
SENCO
- New teacher training
- OR Addressing difficult cases’ behaviour and emotion x 5 small group/1:1 sample
- OR Any concern they like to address

Chapter 6
Domain 5: Parent Engagement
In this chapter, we will discuss how the three distinctive roles (SENCOs, SENST, LSTs) could collaborate to assist the five selected cases in each school in terms of the collaboration with the parents of the cases.
Domain 5: Parent Engagement
TUTORIAL
Introduction
- What are the roles of parents in supporting the five cases?
- How can their involvements be more effective in supporting the five cases?
- How can we assess their involvement?
Roles
SENCO
- Coordination between parents, teachers, LS team and professionals
- Sharing of effective practices and strategies for parents to support child’s learning and development
- Sharing of effective ways to increase effective communication with parents
- Sharing of effective ways to increase parents’ support to the school
SENST
- Communication with parents
- Developing/suggesting suitable activities for parents to do with children to help their learning and development
- Demonstrating and sharing of effective strategies to parents for use at home
LSA
- Communication with parents
- Assist SENST in developing/suggesting suitable activities for parents to do with their children
- Demonstrating and sharing of effective strategies to parents for use at home
Highlights of the discussion
Domain 5: Parent Engagement
SCHOOL VISIT
Introduction
- Discussion with the school’s LS team about their communication with parents for School-based Diversified Learning
SENCO
- Effective practices for parents to support child’s learning and development
- Effective communication with parents
- increase parents’ support to the school
- Assessment mechanism about parents’ engagement
Photo taken with the parent


CHAPTER 7
Real case support exemplifications
Highlight of discussion
Student case (Primary school)
P1
P2
P3
P4
P5
P6

CHAPTER 8
Summary and Participant Feedback
Way forward (future directions in promoting the sustainability of catering for diverse learning needs in schools).
Schools’ expectations upon the LS team’s assistance and expertise:
Asbury Methodist Primary School
- Improve teachers’ mastery and application of adaptive teaching strategies to cope with students’ diverse learning needs
- Strengthen parents’ understanding and support for SPLD students
Hong Kong Red Swastika Society Tai Po Secondary School
- Training and guidance for teaching assistants
- Produce teaching assistant work guidelines to optimize inheritance
Tseung Kwan O Methodist Primary School
- Incorporating cooperative learning and multi-sensory teaching strategies, T2-T1
- Embrace diversity: develop and accept, expand potential
- Mental health: teacher training, I-message admission
Methodist College
T1 teaching planning, parent MI Workshop, whole school teacher workshop, Learning Support Team communicates with teachers from other groups
Baptist (Sha Tin Wai) Lui Ming Choi Primary School
Strengthen classroom design to allow teachers to take care of learning diversity in the classroom and strengthen the culture of whole-school participation and support
Chong Gene Hang College
1. Hope to improve the teaching effectiveness of new teachers
2. Improve classroom management strategies to increase students’ trust in teachers
3. Strategies for building relationships with students
4. Help students improve their learning motivation (some students resist learning)
5. Taking care of students with big differences in three levels, high school, high school and low level, focused development
Caritas Lok Yi School
1. Constructing Cantonese Opera Arts Curriculum (Music Subject)
2. Continue the implementation of IEP in the classroom
Carmel Alison Lam Primary School
1. SENST enrollment collaboration
2. TA admission support
3. SEN student information management
China Holiness College
1. Parent work
– Provide workshops/lectures based on parents’ needs and observe difficulties encountered
– Improve teachers’ skills in dealing with parents
2. Enrollment support
– Optimized guidelines for entry support staff
– Establish guidelines for teaching colleagues
– Test the effectiveness of classroom support
PLK Lee Shing Pik College
My team and I would love to benefit from the expertise and insights of the experience that supervisors and fellow teachers to enhance our team’s ability to cater to learner diversity . We would like to focus on developing in house materials that are still friendly and stimulating for students, various English abilities.
What might be the best Learning Support Model in your school?
1. Resources Management
2. Learning and Teaching Issues
3. Behavorial and Emotional Issues
4. After School Support
5. Parent Support OR
6. Anything you think important
SKH Kowloon Bay Kei Lok Primary School
- Cross-team collaboration enables SEN children to make diverse progress.
- Learning different strategies to care for SEN students.
- Providing SEN children with space and time.
Asbury Methodist Primary School
This year, we initiated parent workshops, where Dr. Ho engaged in heartfelt conversations with SEN students’ parents. During these sessions, she provided them with practical parenting information and offered tangible support. Additionally, Dr. Ho introduced the DMGT Model to us, focusing on developing students’ potential and playing a positive role in their growth.
Lutheran Tsang Shing Siu Leun School
Dr. Leung provided training to teachers and teaching assistants in accordance with our school curriculum this year. The professional development greatly benefited our team of educators. With a keen understanding of the school’s needs, Dr. Leung invested effort and utilized resources to enhance our school.
During collaborative lesson planning, Dr. Leung passionately assisted us in designing classroom activities, shaping our teaching methods, and inspiring reflective thinking among our teachers.
Ma On Shan Methodist Primary School
LS Team can help the school examine the implementation of inclusive education and suggest improvements.
Caritas Lok Yi School
Identifying the challenges, collaborating with the school curriculum and experts to provide targeted support. This can include optimizing curriculum design, instructional strategies, and offering professional training to enhance the overall teaching and learning experience.
SKH St. Michael’s Primary School
Thank you, Dr. Lee, for helping the school.
1. Our school offers after-school support (providing valuable advice and understanding students’ needs).
2. Parent training (providing significant support to parents).
Catholic Ming Yuen Secondary School
The project helps the school examine the current state of teaching and learning for students with needs, support parents in understanding their children, and assess the effectiveness and improvement directions of the SST team.
Fung Kai Innovative School
1. Gain a deeper understanding of students’ learning needs and develop targeted support strategies.
2. Visualize classroom content to aid student learning.
3. Provide training for teaching assistants to enhance the effectiveness of in-class support.
Christian Pui Yan Primary School
L&T: Several three-tiered structure seminars were conducted, providing training for teaching assistants and offering opportunities for school-wide participation. This included case studies of individual students.
Parent Education: Two parent education seminars were held, including sessions specifically for non-Chinese-speaking students’ parents.
HKMLC Queen Maud Secondary School
At the teaching and learning level, more resources are provided, particularly during collaborative lesson planning, where the manager offers appropriate input, including worksheet design and instructional strategies, to cater to diverse learning needs. Through classroom observations and post-lesson reviews, teachers gain a better understanding of their students’ characteristics.
In small group settings, counselors can provide tailored group training, such as social skills training and executive functioning training, for different types of students. The case manager plays a significant role in the professional growth of counselors.
Baptist (Sha Tin Wai) Lui Ming Choi Primary School
Effectively using questioning techniques in the classroom to engage students of different abilities. Analyzing students’ abilities and needs during lesson planning and designing differentiated questions in advance.
L&T support
With professional sharing among teachers and facilitators, teachers include skills in both tier one and two support for students
IEP case support
Through corporation amount, support team, teachers and parents, students, behavioural, and social skills are catered.
Tseung Kwan O Methodist Primary School
Resource management assets base VS problem-solving base
Game-based interventions (executive functioning or teaching and learning)
Creative movement x service learning
Parent x professional training (motivational interviewing approach)
Chi Yun School
It is of great help in student assessment and support, understanding how teaching and learning can be aligned with students’ abilities to engage in activities, and adapting classroom goals in accordance with individualized instruction for students.
Chong Gene Hang College
1. Utilizing VARK to help teachers understand students’ learning styles, providing focused and appropriate instructional content for students.
2. Collaborative lesson planning among teachers to enhance teaching quality.
3. Integrating information technology into teaching to effectively enhance student motivation to learn.
Carmel Alison Lam Primary School
Learning Support Assistant Teacher Handbook
To ensure comprehensive and consistent support for students, a Learning Support Assistant Teacher Handbook has been developed to address the high mobility of assistant teachers. Through professional training for assistant teachers, they are guided in stages to enhance their understanding of their support roles while providing guidance in constructing the Learning Support Assistant Teacher Handbook.
Special thanks to Principal Ching for her patient guidance and valuable input in various aspects!
Hong Kong Red Swastika Society Tai Po Secondary School
Resource Allocation:
Actively introducing external resources and collaborating with external organizations to provide curriculum and activities support.
Teaching and Learning:
Further enhancing the effectiveness of language instruction, optimizing classroom equipment and resources, such as triple-screen teaching, to cater to diverse learning needs.
After-School Support:
Providing professional support to the CLA team during after-school activities.
Methodist College
Individual Support:
- Meeting with students and parents (e.g., IEP cases).
- Positive parental cooperation with the school.
- Students making significant efforts to change.
- Ultimately, students show significant improvement.
Behavior and Emotional Support:
- Allocating more time for personalized follow-up on student progress.
- Managing unexpected situations during free periods.
External Resources:
- Jockey Club “Diversity at Schools” Project (Learning Support Team).
- AIM Project.
After-School Support:
- Enrichment classes (academic improvement).
- Interest-based classes (building peer networks, stress relief).
Caritas Lok Jun School
Addressing school-specific challenges and providing appropriate support. For example, making adjustments to address significant learning differences in the classroom and enhancing learning effectiveness while considering practical classroom instruction and assessment.
S.K.H. Holy Trinity Church Secondary School
Although our participation was relatively brief, we have gained insights into the essence of our school’s future development.
Pun U Association Wah Yan Primary School
We appreciate Principal Ching’s effective analysis of individual students’ learning needs and the collaboration with language teachers to guide them on providing professional and individualized support in the classroom or within the IEP. This includes in-class support, adapting worksheets, and more.
Furthermore, an effective consolidation of existing after-school support or student support summaries in written form would facilitate the transfer of support knowledge to other teachers efficiently.
What is the planning of a good Learning Support Model for your school in the future?
1. Resources Management
2. Learning and Teaching Issues
3. Behavorial and Emotional Issues
4. After School Support
5. Parent Support OR
6. Anything you think important
Christian Pui Yan Primary School
Mentor: Pairing up colleagues within the school.
Inter-school pairing/networking.
SWOT analysis of the school’s internal situation.
Resource management: Handbooks (highlighting work priorities) with a focus on TA training.
Teaching and Learning: Lectures, resource sharing, transitioning from tier 2 or 3 to tier 1.
For L&T support
Formation of learning circle
Some new teachers who receive support in this year would be facilitators for new teachers, such that the strategies and experience could be passed on.
Stewards Pooi Kei College
Continue inviting teachers to become seed teachers and have external experts or senior colleagues within the school lead them in classroom research. Continue experimenting with different methods and encourage teachers to bring their experiences back to the subject groups.
Externally, utilize school communication channels or parent seminars to make parents aware of the school’s philosophy and work.
Caritas Lok Yi School
1. Enhancing teaching methodologies.
2. Providing feedback on the curriculum.
3. Optimizing classroom elements such as learning methods, subject components, and facilitating student learning.
4. Transferring subject knowledge acquired through learning to other disciplines and continuing to enhance the platform.
5. Centralizing all subject materials on the platform and exchanging knowledge with different schools for sharing, promotion, and optimization of the entire curriculum.
Chong Gene Hang College
– Implementing VARK model throughout the school and enhancing differentiated instructional support.
– Engaging in academic exchanges with other schools.
– Strengthening teacher training for improving teaching quality.
CCC Rotary Secondary School
Pre-class instructional lesson planning.
Classroom teaching and appropriate scheduling with differentiated assignments.
Follow-up and feedback on challenging topics after class, arranging self-learning resources for knowledge consolidation.
Baptist (Sha Tin Wai) Lui Ming Choi Primary School
In the collaborative lesson preparation, textbook, and presentation for teachers, incorporate questions at different levels to allow students with varying learning abilities to attempt answering and engage in the classroom.
Teachers participating in the program can also share their teaching experiences with other teachers during subject meetings or at the end of the semester, allowing other teachers to learn about the content of the program.
HKMLC Queen Maud Secondary School
– more workshops regarding inclusive teaching practices
– create quiet zones and collaborative spaces
– integrate mental health education into curriculum, such as religious study
– establish programs to recognise positive behaviour and academic achievements
– conduct workshops on supporting children’s emotional and academic needs
Tseung Kwan O Methodist Primary School
Game-based interventions (executing functions or teaching and learning).
Creative movement and service learning (emphasizing strengths).
Teacher/parent professional training (motivational interviewing approach).
Methodist College
Whole-school support (process arrangement).
Remedial classes (targeting designed SEN curriculum).
Collaboration with various subjects for after-school support programs.
Po Leung Kuk Lee Shing Pik College
Learning and teaching in curriculum development
1. More support for Newly joined teachers to cater for learning diversity: (a) material development (b) how to adapt in-house materials for use in their classrooms (c) supportive lesson, observations to facilitate discussion within the department.
2. Continued professional development to stay abreast of the latest pedagogies and EDB initiatives.
Hong Kong Red Swastika Society Tai Po Secondary School
Continue utilizing and improving the CLA handbook to support current and new CLAs.
Maintain the dedicated CLA professional exchange time on Fridays, allowing them to share success stories (student support, instructional assistance) with each other. The school will provide more opportunities for CLAs to share, such as SDD, to enhance the effectiveness of professional exchanges and elevate the professional image of the CLA team.

CHAPTER 9 Acknowledgement
(in no particular order)
The Hong Kong Jockey Club Charities Trust
Principal POON Kai Cheung, Franky (PI)
Core Schools
Asbury Methodist Primary School
Fanling Assembly of God Church Primary School
Hong Kong Red Swastika Society Tai Po Secondary School
Kit Sam Lam Bing Yim Secondary School
Pun U Association Wah Yan Primary School
Tseung Kwan O Methodist Primary School
DM Schools
Year 2
Baptist (Sha Tin Wai) Lui Ming Choi Primary School
C.C.C.Fung Leung Kit Memorial Secondary School
Caritas Lok Yi School
China Holiness College
Chiu Chow Association Secondary School
Cho Yiu Catholic Primary School
Cotton Spinners Association Secondary School
Fung Kai Innovative School
HKCKLA Buddhist Ching Kok Lin Association School
HKMLC Queen Maud Secondary School
HKSKH Bishop Hall Secondary School
HKUGA Primary School
Hong Kong Sea School
Hong Kong Student Aid Society Primary School
Ju Ching Chu Secondary School (Tuen Mun)
Lutheran Tsang Shing Siu Leun School
Man Kwan Pak Kau College
Methodist College
PLK Dr. Jimmy Wong Chi-Ho (Tin Sum Valley) Primary School
Precious Blood Primary School
Pui Kiu College
San Wui Commercial Society Secondary School
Sir Ellis Kadoorie Secondary School (West Kowloon)
St. Peter’s Secondary School
The Salvation Army William Booth Secondary School
Tsang Pik Shan(Sung Lan)Secondary School
Tsz Wan Shan Catholic Primary School
DM Schools
Year 3
Baptist (Sha Tin Wai) Lui Ming Choi Primary School
Caritas Lok Jun School
Caritas Lok Yi School
Carmel Alison Lam Primary School
Catholic Ming Yuen Secondary School
CCC Rotary Secondary School
Chi Yun School
China Holiness College
Chiu Chow Association Secondary School
Cho Yiu Catholic Primary School
Chong Gene Hang College
Christian Pui Yan Primary School
Chun Tok School
Cotton Spinners Association Secondary School
ELCHK Hung Hom Lutheran Primary School
Fanling Government Secondary School
Fung Kai Innovative School
GCCITKD Cheong Wong Wai Primary School
Heung To Middle School
HKMLC Queen Maud Secondary School
HKSKH Bishop Hall Secondary School
HKUGA Primary School
Ju Ching Chu Secondary School (Tuen Mun)
Lingto Catholic Primary School
Lutheran Tsang Shing Siu Leun School
Ma On Shan Methodist Primary School
Man Kwan Pak Kau College
Methodist College
PLK Dr. Jimmy Wong Chi-Ho (Tin Sum Valley) Primary School
Po Leung Kuk Lee Shing Pik College
Pui Kiu College (Primary Section)
S.K.H. Kowloon Bay Kei Lok Primary School
S.K.H. St. Andrew’s Primary School
S.K.H. St. John’s Tsang Shiu Tim Primary School
S.K.H. St. Matthew’s Primary School
S.K.H. St. Michael’s Primary School
Sir Ellis Kadoorie Secondary School (West Kowloon)
SKH Holy Trinity Church Secondary School
St. Edward’s Catholic Primary School
Stewards Pooi Kei College
Tsang Pik Shan(Sung Lan)Secondary School
Tsuen Wan Trade Association Primary School
Tsz Wan Shan Catholic Primary School
The University of Hong Kong (HKU) Evaluation and Dissemination Team
The University of Hong Kong (HKU) Differentiated Instruction Team
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) Student Data Team
The Education University of Hong Kong (EdUHK)
President
Professor LEE, Chi Kin John, JP
The Education University of Hong Kong (EdUHK)
Faculty of Education and Human Development
Dean, Faculty of Education and Human Development
Professor MACFARLANE, Bruce John
The Education University of Hong Kong (EdUHK)
Department of Special Education & Counselling
Associate Professor, Acting Head of Department
Dr. YUM Yen Na, Cherry
Project Investigator, Learning Support Team
Dr. CHIM Ho Yeung, Hastings
Consultant, Learning Support Team
Dr. HO Fuk Chuen
School Case Manager
Mr. CHAN Wai Man, Avstin
School Case Manager
Principal CHING Sau Man
School Case Manager
Ms. FUNG Kwei Yi, Jessie
School Case Manager
Dr. HO Pik Ying
School Case Manager
Principal LAU Hor Keung
School Case Manager
Dr. LEE Lai Mui, Frances
School Case Manager
Dr. LEUNG Sheung Kwan, Sharon
School Case Manager
Dr. Siu Fung LIN
School Case Manager
Mr. SO Kin Kwan, Kennith
School Case Manager
Mr. WONG Chun Man, Vincent
Assistant Project Manager
Ms. TAM Gee May
Project Assistant
Ms. Ng Lok Yiu, Yoyo
Project Assistant
Ms. Hui Cheuk Lam, Zena
版權所有 不得轉載 © 2018-2022 賽馬會「校本多元」計劃





